Contents
- Outline of tree
- Terminology
- terms
- Implementation
- Traversal algorithms
- Depth-first traversal
- Level-order traversal
- Search
- Reference
Outline of tree
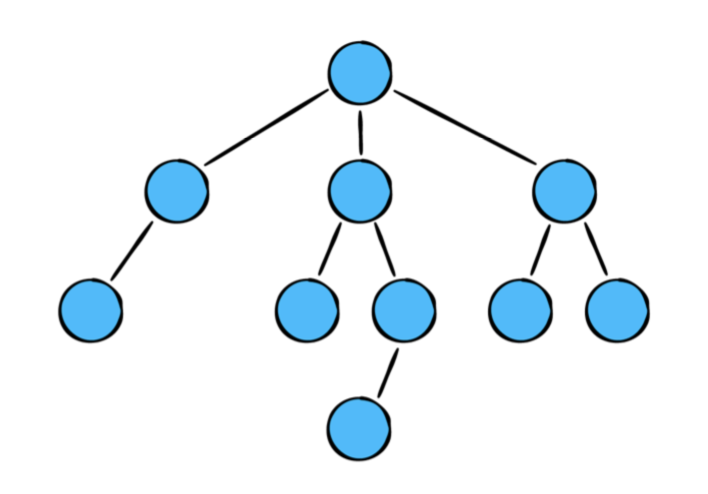
트리는 자료구조에서 중요합니다. 소프트웨어 개발에서 반복되는 여러가지 문제들은 해결합니다
- 계층관계를 나타내는 것
- 정렬된 데이터를 관리하는 것
- 검색 작업을 수월하게 하는 것
여기에는 많은 트리의 타입들이 있는데, 그 트리들은 다양한 모양과 사이즈를 가집니다.
Terminology
terms
- Root: 트리의 최상위에 있는, 부모 노드를 지니지 않은 유일한 노드를 가르킵니다.
- Node: 자식 노드와 부모 노드에 대한 참조 데이터(혹은 레퍼런스), 그리고 값을 지닌 데이터 구조 입니다. 만일 어떤 노드가 부모 노드에 대한 참조 데이터가 없다면, 바로 그 노드가 트리의 루트 노드가 됩니다. 또 어 떤 노드가 자식 노드를 지니지 않았을 경우 잎사귀 노드(Leaf node)가 됩니다.
- Edge: 부모 노드와 자식 노드 의 연결선을 가르킵니다
- Parent: 다른 노드와 연결돼 있으면서, 계층 구조상 특정 노드의 바로 위에 있는 노드를 가리킵니다. 모든 노드는 오직 하나(혹은0) 이 부모를 지닙니다.
- Child: 다른 노드와 연결 돼 있으면서, 계층 구조상 특정 노드의 바로 아래에 있는 노드를 가르킵니다. 모든 노드는 0개의 혹은 여러개의 자식 노드를 지닙니다.
- Sibling: 동일한 부모 노드에서 나온 노드를 가리킵니다.
- Leaf: 더 이상 자식 노드를 지니지 않은(노드의 종단점인) 자식 노드를 가리키며, 트리 계층 구조에서 맨 아래에 위치합니다. 잎 노드는 외부 노드(external node)로 잎 사귀 노드가 아닌 노드는 내부 노드(internal node)로 부릅니다
- Subtree: 특정 노드의 모든 자손을 가리킵니다
- Height of a node: 하나의 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어져 있는 잎사귀 노드에 이르는 모서리 수를 가리킵니다. 루트 노드밖에 없는 트리의 노드 높이는 0 입니다
- Height of a tree: 루트 노드에서 잰 높이입니다.
- Depth: 루트와 노드를 연결하는 모서리의 수를 가리킵니다
- Level: 어떤 노드의 레벨이란 깊이 +1을 의미합니다
- Tree traversal: 트리의 모든 노드를 한번씩 다녀오는 과정을 의미합니다.
Implementation
// helper
public func example(of description: String, action: () -> Void) {
print("---Example of \(description)---")
action()
print()
}
// 1
public class TreeNode<T> {
public var value: T
public var children: [TreeNode] = []
public init(_ value: T) {
self.value = value
}
public func add(_ child: TreeNode) {
children.append(child)
}
}
// 2
extension TreeNode: CustomStringConvertible {
public var description: String {
return "value: \(self.value)"
}
}
// 3
example(of: "creating a tree") {
let beverages = TreeNode("Beverages")
let hot = TreeNode("Hot")
let cold = TreeNode("Cold")
beverages.add(hot)
beverages.add(cold)
}
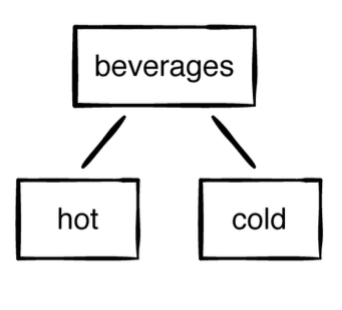
구현방법에는 여러가지가 있지만, 여기에서는 자식 노드의 참조를 배열로했습니다..
Traversal algorithms
배열이나 Linked List 같은 선형 컬랙션을 순회하는것을 간단합니다. 선형 컬랙션에는 명확한 시작과 끝이 있습니다.
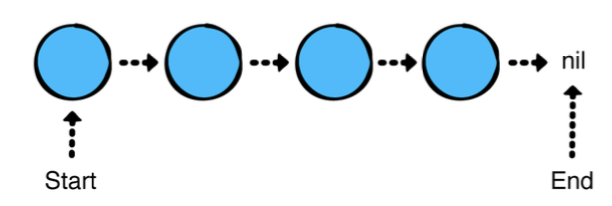
하지만 트리를 순회하는것은 조금 복잡합니다.
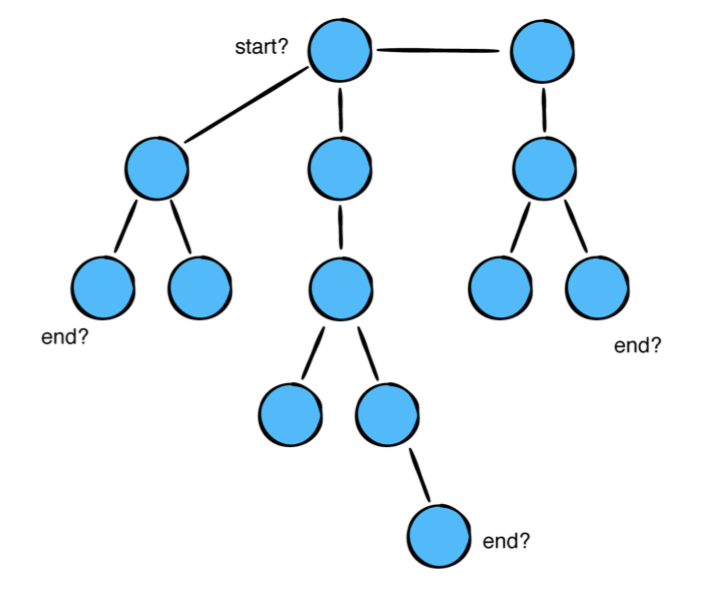
어떤 노드를 우선으로 해야하나요? 왼쪽 노드 인가요? 노드의 깊이(depth of a node)가 우선 순위와 어떤 관련이 있나요? 순회전략은 문제를 어떻게 해결할것인지에 달려 있습니다.
Depth-first traversal
// 1
extension TreeNode {
public func forEachDepthFirst(visit: (TreeNode) -> Void) {
visit(self)
children.forEach { $0.forEachDepthFirst(visit: visit) }
}
}
// 2
func makeBeverageTree() -> TreeNode<String> {
let tree = TreeNode("Beverages")
let hot = TreeNode("hot")
let cold = TreeNode("cold")
let tea = TreeNode("tea")
let coffee = TreeNode("coffee")
let chocolate = TreeNode("cocoa")
let blackTea = TreeNode("black")
let greenTea = TreeNode("green")
let chaiTea = TreeNode("chai")
let soda = TreeNode("soda")
let milk = TreeNode("milk")
let gingerAle = TreeNode("ginger ale")
let bitterLemon = TreeNode("bitter lemon")
tree.add(hot)
tree.add(cold)
hot.add(tea)
hot.add(coffee)
hot.add(chocolate)
cold.add(soda)
cold.add(milk)
tea.add(blackTea)
tea.add(greenTea)
tea.add(chaiTea)
soda.add(gingerAle)
soda.add(bitterLemon)
return tree
}
// 3
example(of: "depth-first traversal") {
let tree = makeBeverageTree()
tree.forEachDepthFirst { print($0.value) }
}
// 4
---Example of: depth-first traversal---
Beverages
hot
tea
black
green
chai
coffee
cocoa
cold
soda
ginger ale
bitter lemon
milk
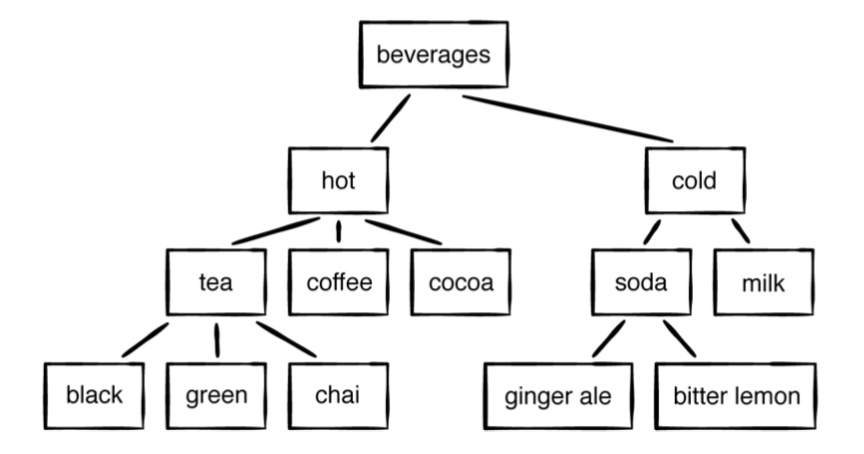
루트 노드에서 시작하여, 각 자식 노드 -> 각 자식노드 끝까지 내려가서 더이상 자식 노드가 없을때 해당 나머지 값들을 순차적으로 순회합니다.
Level-order traversal
// helper
public protocol Queue {
associatedtype Element
mutating func enqueue(_ element: Element) -> Bool
mutating func dequeue() -> Element?
var isEmpty: Bool { get }
var peek: Element? { get }
}
public struct QueueArray<T>: Queue {
private var array: [T] = []
public init() {}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
return array.isEmpty
}
public var peek: T? {
return array.first
}
public mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) -> Bool {
array.append(element)
return true
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
return isEmpty ? nil : array.removeFirst()
}
}
extension QueueArray: CustomStringConvertible {
public var description: String {
return array.description
}
}
// 1
extension TreeNode {
public func forEachLevelOrder(visit: (TreeNode) -> Void) {
visit(self)
var queue = Queue<TreeNode>()
children.forEach { queue.enqueue($0) }
while let node = queue.dequeue() {
visit(node)
node.children.forEach { queue.enqueue($0) }
}
} }
// 2
example(of: "level-order traversal") {
let tree = makeBeverageTree()
tree.forEachLevelOrder { print($0.value) }
}
// 3
---Example of: level-order traversal---
beverages
hot
cold
tea
coffee
cocoa
soda
milk
black
green
chai
ginger ale
bitter lemon
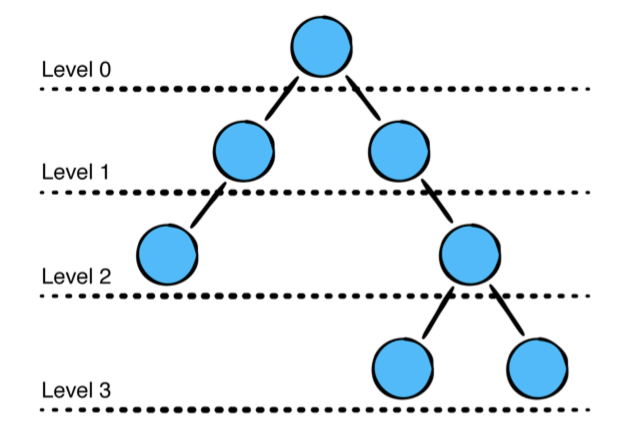
각 레벨을 순차적으로 순회합니다.
Search
위의 순회하는 방법을 이용해서 Search를 구현합니다
// 1
extension TreeNode where T: Equatable {
public func search(_ value: T) -> TreeNode? {
var result: TreeNode?
forEachLevelOrder { node in
if node.value == value {
result = node
}
}
return result
}
}
// 2
example(of: "searching for a node") {
// tree from last example
if let searchResult1 = tree.search("ginger ale") {
print("Found node: \(searchResult1.value)")
}
if let searchResult2 = tree.search("WKD Blue") {
print(searchResult2.value)
} else {
print("Couldn't find WKD Blue")
}
}
// 3
--Example of: searching for a node---
Found node: ginger ale
Couldn't find WKD Blue
여기서는 level-order traversal 알고리즘을 사용 했습니다. 만약, 동일한 값이 여러개라면, 맨 마지막 값을 기준으로 반환합니다. 즉 어떤 순회를 사용하느냐에 따라서 다른 오브젝트를 다시 얻게된다는걸 의미합니다.(고칠점도 많다는 뜻..)
Reference
swift-algorithm-club/Tree
Data Structures and Algorithms in Swift