Code
func example(str: String, isAction: Bool = true, action: () -> Void) {
print("---------\(str), isAction: \(isAction)---------")
if isAction {
action()
}
}
func createRandomArray(numberOfElements: Int = 10) -> [Int] {
var randomIntInArray: [Int] = [Int]()
while randomIntInArray.count != numberOfElements {
let popRandomValue = Int(arc4random_uniform(11))
randomIntInArray.append(popRandomValue)
}
return randomIntInArray
}
example(str: "Bubble Sort", isAction: true) {
func bubbleSort<T: Comparable>(data: [T]) -> [T] {
guard data.count > 1 else { return data }
var totalCounter: Int = 0
var targetData = data
for i in 0..<(targetData.count-1) {
for j in 0..<(targetData.count-i-1) {
if targetData[j] > targetData[j+1] {
print("i:\(i), j:\(j), 비교대상: \(data[j]) > \(data[j+1]), 정렬대상: \(data)")
// 서로의 Index로 값 스왑∑
targetData.swapAt(j, j+1)
// Count up
totalCounter += 1
}
}
}
print("총순회 횟수: \(totalCounter), 입력 데이터 길이\(data.count), 결과:\(data)")
return targetData
}
print(bubbleSort(data: createRandomArray(numberOfElements:10)))
}
- bubbleSort는 예를들어서 데이터 개수가 10개이면 2개의 대상씩 비교를하는데, 10x10 비교 하지않고,
- 0 -> 0~9
- 1 -> 0~8
- 2 -> 0~7
- ….
- 8 -> 0
- 배열의 맨 마지막은, 인덱스를 n-1에서 교환(쌍으로 비교하기때문에 마지막 인덱스를 필요없음)이 이루어지고, 어떤 대상이 비교되어지면서 있어야할 자리에 있게 되면, 그부분은 더이상 정렬하지 않음
- 데이터의 길이가 10개이면 총 순회 횟수 9+8+7…0
- 데이터 길이가 100개이면 총 순회 횟수 99+98+97…0
Time Complexity
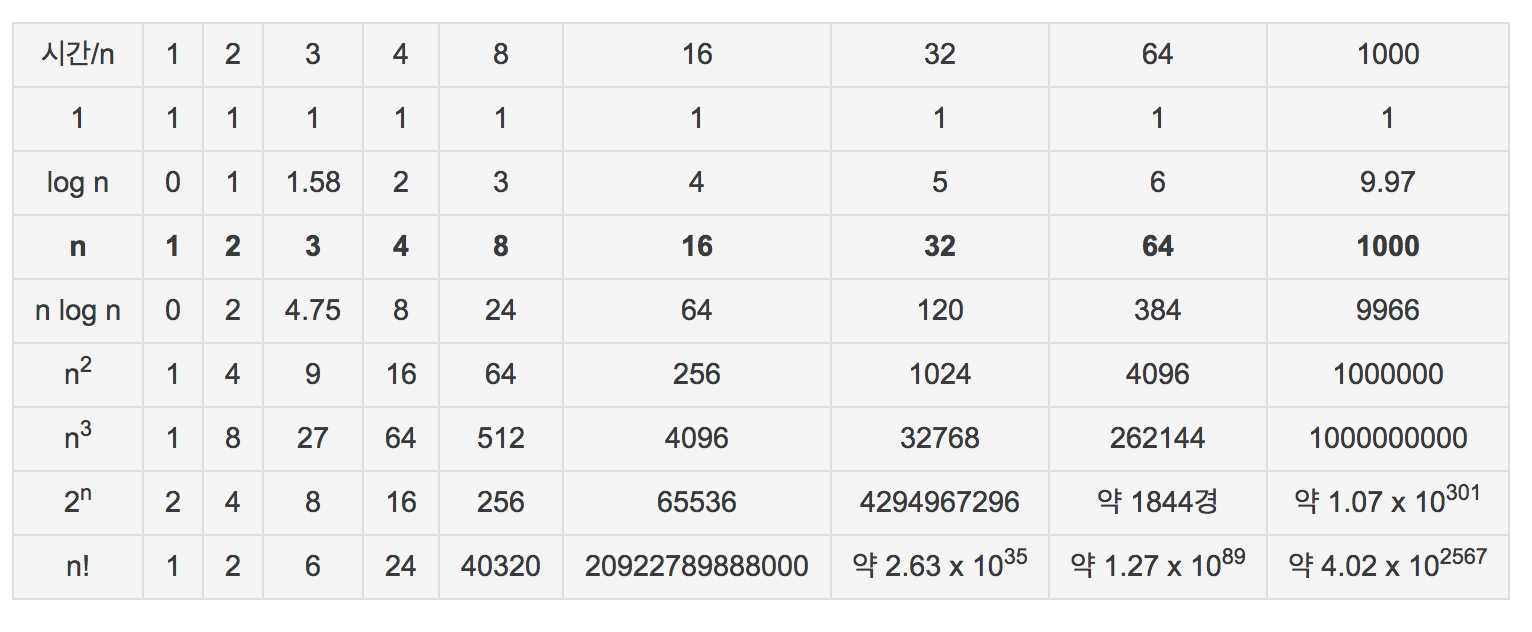
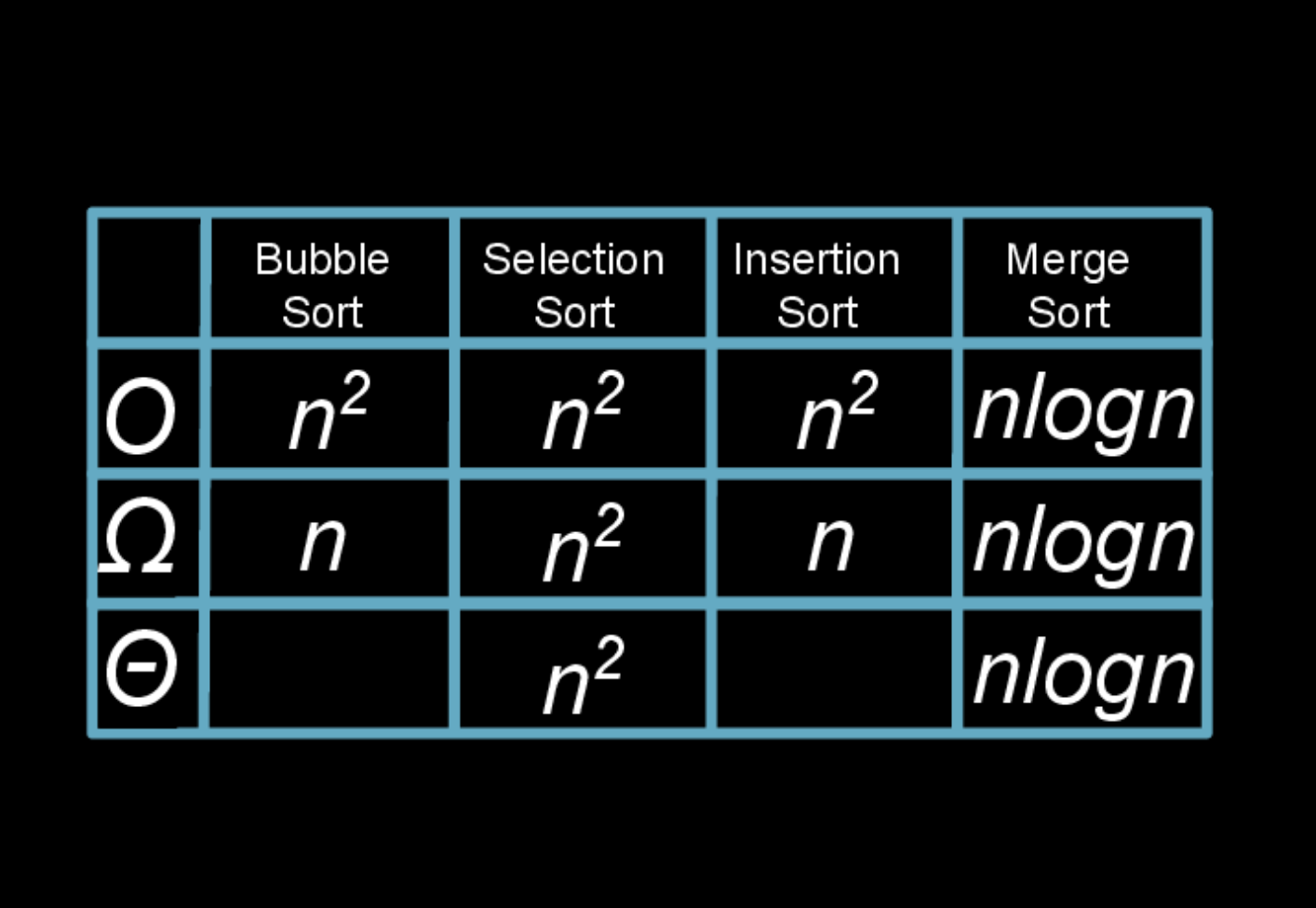
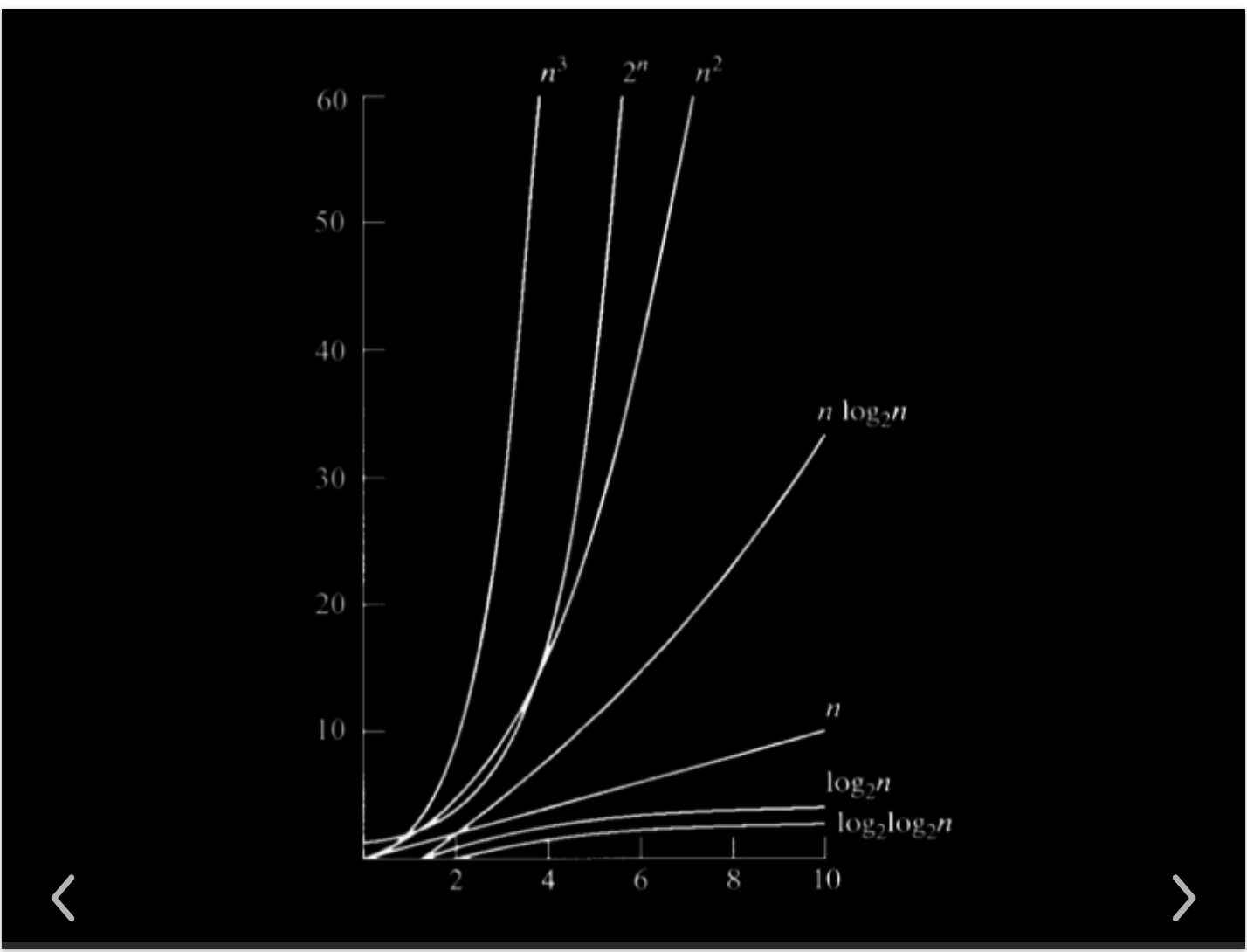
Reference
https://www.dropbox.com/s/l55ili5bzjsm34e/Bubble%20Sort.pdf?dl=0